2. Taiji, Japan
8. Bang the pole with hammers to frighten dolphins then the fishermen would surround the dolphins to trap them.
9. Some are auctioned off to different dolphin trainers from different places at high prices.
10. 23 000 dolphins killed
12. Mercury
Park's Biology Blog
Friday, 2 December 2011
Response To Shark Fin Article
I strongly support the ban on shark fin and do not agree with the complaints. First of all, the city councilors voted 38 – 4 to ban the consumption of shark fins in Toronto. This indicates that majority of the local communities do consider killing sharks as a despicable action and support banning consumption of shark fins. Moreover, due to people’s greed, 90% of the shark population has decreased and I think it is time for more countries and citizens to be active in protecting the remaining sharks. In fact, I think that sharks are really important creatures for humans because they have been on Earth for more than 400 million years (older than dinosaurs). Therefore, sharks can provide lots of information to scientists relevant to evolution and the history of Earth, which is why I am suggesting that they should be considered as an international treasure.
By banning shark fin products in Toronto, it does not completely disrupt the Chinese culture, which is what many Chinese – Canadians feel. Also, I am certain that there are many other foods that can replace shark fin soups for weddings or any other important events. I do understand that some people value every part of their culture greatly. However, I think that it is more important to protect sharks before all species become extinct. I strongly support the verdict that was made by the councilors and they should continue to conserve all shark species not only for our generation but for future generations.
Sunday, 13 November 2011
Thursday, 20 October 2011
20 Key Points From Page 58 ~ 77
1. Catabolic reaction is a reaction that results in the breakdown of complex substances.
Anabolic reaction is when complex substances from simpler forms are constructed.
Metabolism = All anabolic and catabolic processes in a cell/organism.
2. First Law of Thermodynamics: The total amount of energy in the universe is constant. Energy cannot be created or destroyed but only converted from one form into another.
3. Second Law of Thermodynamics: The entropy of the universe increases with any change that occurs.
4. All forms of energy can be categorized as kinetic energy, the energy possessed by a moving object, or potential energy which refers to the stored energy. Some forms of kinetic energy include thermal energy, mechanical energy, electrical energy and electromagnetic energy. Some examples of potential energy are gravitational potential energy and chemical potential energy.
5. Bond energy is a measure of the stability of a covalent bond and is measured in kilojoules (kJ). Bond energy equals to the minimum energy required to break one mole of bonds between two types of atoms. It also indicates the amount of energy released when a bond is formed.
6. Activation energy is the difference between the potential energy level of transition state and the potential energy of reacting molecules.
Transition state is a temporary condition during a chemical reaction in which the bonds within reactants are breaking and the bonds between products are forming.
7. If the bonds in products are more stable than those in the reactants, more energy is released during bond formation than was absorbed during bond breaking. As a result, this will result in a net energy output and this reaction is known as an exothermic reaction.
8. When the amount of energy absorbed in breaking reactant bonds is greater than the energy released in the formation of product bonds, it results in a net absorption of energy. This reaction is called an endothermic reaction.
9. Entropy refers to a measure of the randomness or disorder in energy or in a system.
In chemical reactions, entropy increases when:
- solid reactants become liquid or gaseous products
- liquid reactants become gaseous products
- fewer moles of reactant molecules form a greater number of moles of product molecules
- complex molecules react to form simpler molecules (polymers into monomers, or glucose into carbon dioxide and water)
- solutes move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration until they are uniformly distributed in the given volume (diffusion)
10. Exergonic reaction is spontaneous and is accompanied by a decrease in Gibbs free energy. (
11. Endergonic reaction is not spontaneous and is accompanied by an increase in Gibbs free energy. ( Change in Gibbs free energy is positive)
12. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the primary source of free energy in living cells.
13. Phosphorylation is the process of attaching a phosphate group to an organic molecule.
14. Oxidation is when an atom loses one or more electrons during a chemical reaction. Reduction is when an atom gains one or more electrons.
15. An electron transfer between two substances always involves an oxidation and a reduction and this is known an redox reaction.
16. Substrate is the reactant that an enzyme acts on when it catalyzes a chemical reaction. The active site is the location where the substance binds to an enzyme (protein catalyst).
17. Many substances inhibit enzyme activity. Competitive inhibitors enter the enzyme’s active site and block the normal substrate from binding.
18. Non competitive inhibitors attach to another site on the enzyme (not the active site), causing a change in the enzyme’s shape. As a result, the changes in active site in such a way that it loses affinity for its substrate.
19. Feedback inhibition is a method used by cells to control metabolic pathways in which a product formed later in the sequence of reactions allosterically inhibits an enzyme that catalyzes a reaction occurring earlier in the process.
20. Cells control metabolic processes by restricting the location of enzymes and enzyme complexes to certain locations within the cell.
10 Key Points For Biotech Test
Vector Cloning
- Recombinant DNA is a fragment of DNA composed of sequence originating from at least two different sources.
- Same restriction enzyme is utilized to cut the DNA and the plasmid in order to form a sticky ends.
Gel Electrophoresis
- Since DNA is negatively charged, they travel to the positively charged end of the gel electrophoresis.
- Shorter the fragment, it will travel closer to the positive end and larger fragments will remain closer to the negative end of gel electrophoresis.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- In PCR process, Taq polymerase is used to build complementary strands using free nucleotides that have been added to the solution. Taq polymerase can withstand high temperatures without being denatured.
- By the end of 3rd cycle, first two copies of targeted strand are formed. By the third cycle, the number of copies of the targeted strand begins to increase exponentially.
(Click to see a video that explains the process of PCR. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_YgXcJ4n-kQ )
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
- RFLP involves the comparison of different lengths of DNA fragments produced by (a) restriction enzyme(s).
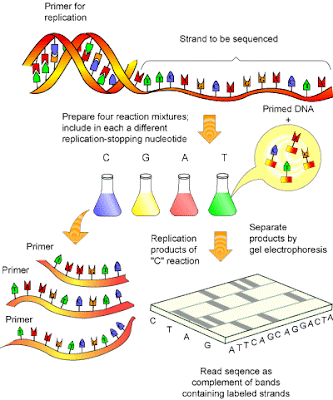
DNA Sequencing
- Dideoxynucleotides cause the new strand of DNA to terminate at various points due to the absence of hydroxyl group attached to the 3’ carbon.
- The result (autoradiogram) can be used for forensic science or detect a mutation that has a potential of causing a genetic disorder.

PCR vs DNA Sequencing
Similarities
· Both techniques use DNA polymerase and primers for elongation.
· Gel electrophoresis is used to separate the different lengths of DNA produced at the end of both processes.
PCR
· Utilizes a special polymerase called taq polymerase which can withstand high temperature.
· Instead of RNA primer, DNA primers are use to initiate the elongation.
· Heating is used to break the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases, forming single stranded DNA.
DNA Sequencing
· Dideoxynucleotides cause the new strand of DNA to terminate at various points due to the absence of hydroxyl group attached to the 3’ carbon.
Monday, 10 October 2011
PCR VS Vector Cloning
SIMILARITIES
1. Both techniques are used to a DNA segment that contains the gene of interest and make copies of them.
2. The number of copies of targeted strands begins to increase exponentially.
DIFFERENCE
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction
1. Direct method of amplifying copies of a desired DNA sequence without using cells.
2. PCR requires three steps:
Heating – As temperature rises in the range of 94 – 96 degrees Celsius, the hydrogen bonding between nitrogen bases break causing the DNA strands to separate.
Cooling – Temperature is cooled down to the range of 50 – 65 degrees Celsius for the primers to anneal with the strands (template DNA).
Replication – A special DNA polymerase builds complementary strands using free nucleotides and the elongation is initiated by DNA primers.
3. Taq polymerase, which is isolated from a bacterium that lives in hot springs, is used to elongate the new DNA strand.
4. PCR requires less time compared to the vector cloning.
5. By the third cycle, the number of copies of the targeted strands begins to increase exponentially.
Vector Cloning
1. Appropriate restriction enzymes are needed to excise a gene fragment from the source DNA. More than one RE may b used at one time.
2. A plasmid of a bacterium is cut open using a RE, producing sticky ends. Then DNA fragment and plasmid is joined by DNA ligase.
3. Bacterium is used often utilized as a host organism because they reproduce fast, easy to obtain and their plasmid is very stable.
4. The introduction of DNA from another source into a host cell is known as transformation.
5. Vector cloning is relatively cheaper than PCR.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)