Vector Cloning
- Recombinant DNA is a fragment of DNA composed of sequence originating from at least two different sources.
- Same restriction enzyme is utilized to cut the DNA and the plasmid in order to form a sticky ends.
Gel Electrophoresis
- Since DNA is negatively charged, they travel to the positively charged end of the gel electrophoresis.
- Shorter the fragment, it will travel closer to the positive end and larger fragments will remain closer to the negative end of gel electrophoresis.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- In PCR process, Taq polymerase is used to build complementary strands using free nucleotides that have been added to the solution. Taq polymerase can withstand high temperatures without being denatured.
- By the end of 3rd cycle, first two copies of targeted strand are formed. By the third cycle, the number of copies of the targeted strand begins to increase exponentially.
(Click to see a video that explains the process of PCR. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_YgXcJ4n-kQ )
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
- RFLP involves the comparison of different lengths of DNA fragments produced by (a) restriction enzyme(s).
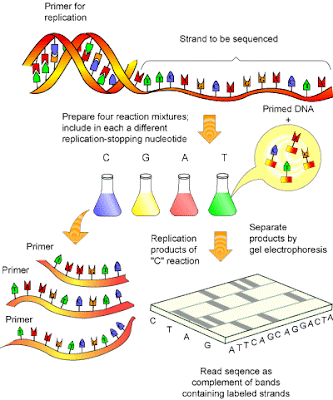
DNA Sequencing
- Dideoxynucleotides cause the new strand of DNA to terminate at various points due to the absence of hydroxyl group attached to the 3’ carbon.
- The result (autoradiogram) can be used for forensic science or detect a mutation that has a potential of causing a genetic disorder.


No comments:
Post a Comment